What foods have phosphatidylcholine?
Today we are going to see which food have phosphatidylcholine. Firstly understand that Eggs, fish, and meat were the main sources of phosphatidylcholine (28.0%, 18.5%, and 18.3% respectively). These items contributed a total of 65% of the phosphatidylcholine that was consumed. Meat (28.5%), dairy (23.3%), and fish (21.7%) were the dietary categories that contributed the most to sphingomyelin in the diet. Dairy, beverages, grains, and vegetables were the main sources of free lecithin.
Why phosphatidylcholine is important
A nutrient called lecithin is essential for the development of the brain, neurotransmitter synthesis, metabolism, and other body functions.
The modest amounts of this nutrient that your body naturally produces are insufficient to meet your needs, therefore you must consume some in your diet. Fortunately, a lot of foods made from both plants and animals contain this nutrient.
Let’s see the list of food have phosphatidylcholine in it
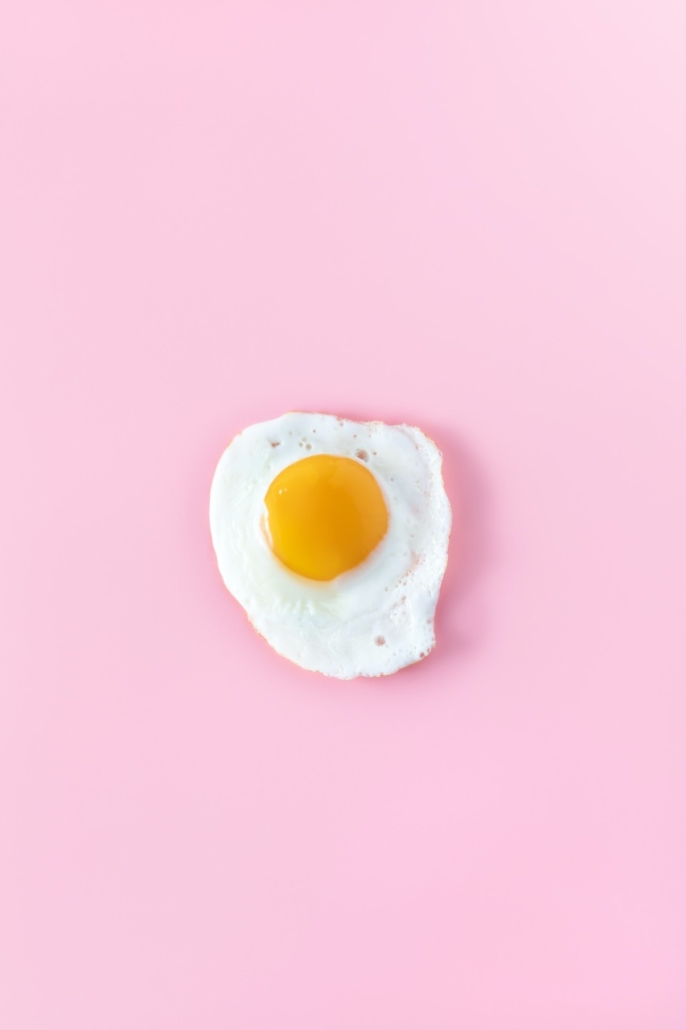

Whole eggs
- One egg provides 147 mg of choline, making it one of the greatest sources. This indicates that eating just two eggs daily provides 54% of the recommended daily intake (RDI).
- The yolk of an egg contains almost all of its lecithin content. Consume the entire egg to get the maximum choline because there are 680 mg of the nutrient in egg yolks for every 100 grams compared to 1 mg in egg whites
- According to studies, lecithin contained naturally in eggs may be more easily absorbed than choline provided in nutritional supplements.
- This is so because eggs contain choline that is attached to phospholipids, a form of fat. It has elements that are both hydrophilic (having an attraction for water) and hydrophobic (having an aversion to water), allowing your digestive tract to immediately absorb them.
Fish
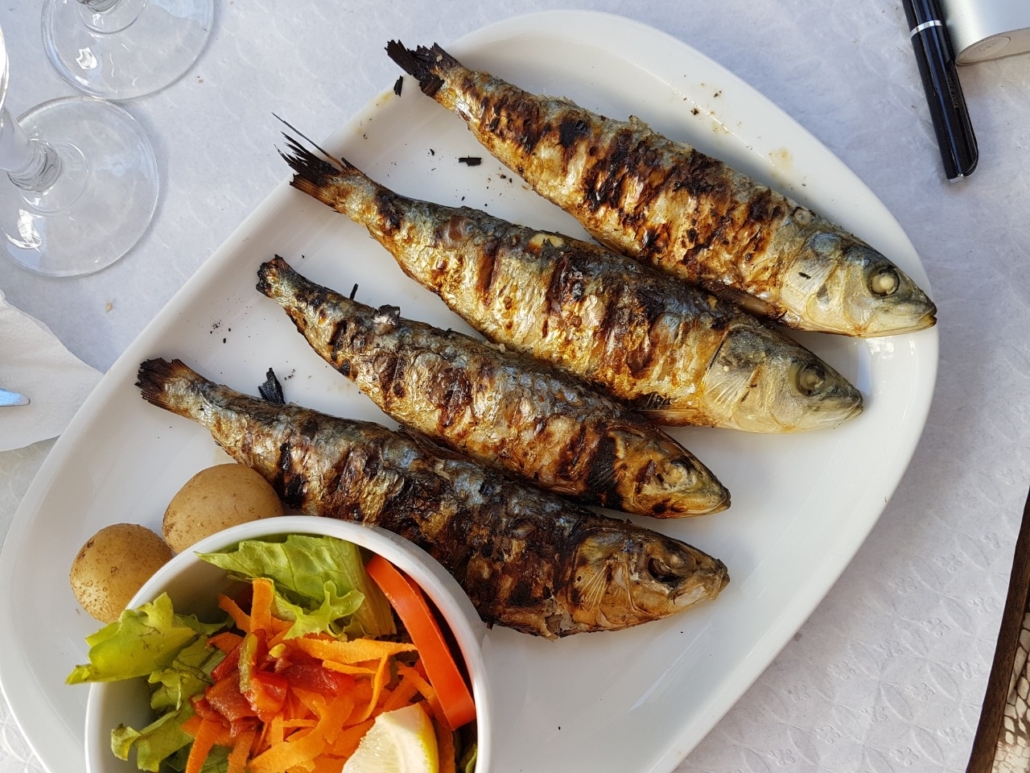

- Choline is in seafood, such as salmon, tuna, and cod fish. For instance, 187 mg, or 34% of your daily needs, are provided by 3 ounces (85 grams) of salmon.
- The fact that some studies have linked a reduced fish intake with decreased blood lecithin levels in particular groups may therefore not come as a surprise.
- For instance, a study of 222 pregnant women revealed that those who had 75 grams or less of fish weekly had lower blood levels of lecithin, DHA, and vitamin D compared to those who ingested 150 grams or more of fish weekly.
- Phospholipids are commonly found in fish species in amounts between one and five percent, while krill often has forty percent. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), two omega-3 fatty acids included in krill oil, have been said to be more bioavailable than those found in fish oil.
Shiitake mushrooms
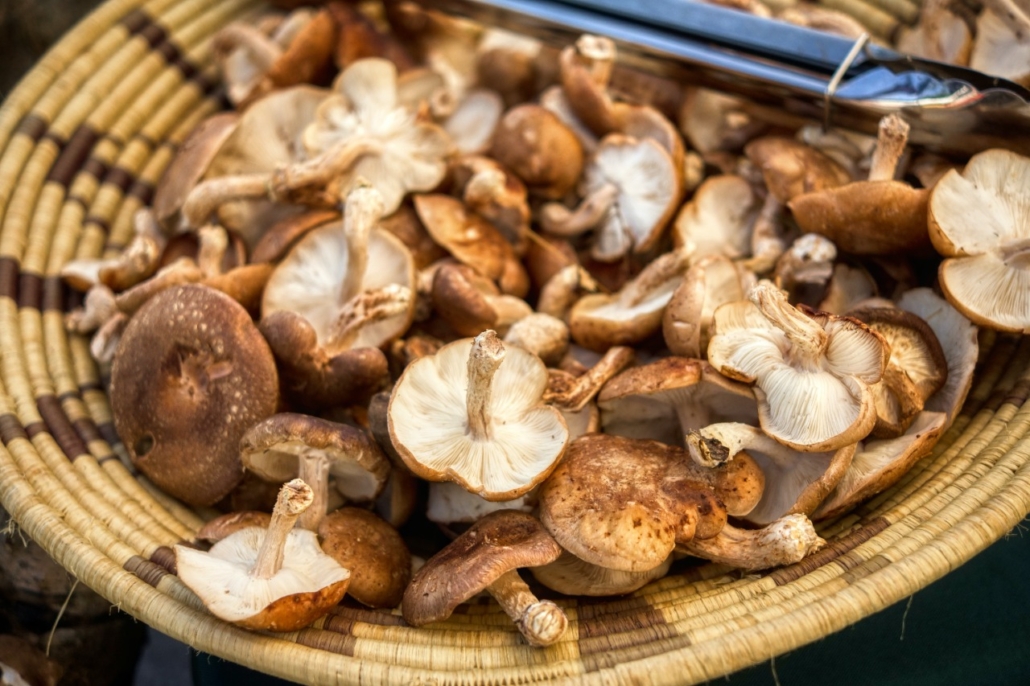

- These mushrooms are a fantastic source of choline from plants and have an outstanding range of other nutrients.
- Shiitake mushrooms cooked in a cup (145 grams) supply 116 mg, or 21% of your daily needs.
- Shiitake mushrooms are also abundant in vitamins and minerals including selenium, copper, and vitamin B5, and studies indicates that eating them may improve immunological function.
Soybeans
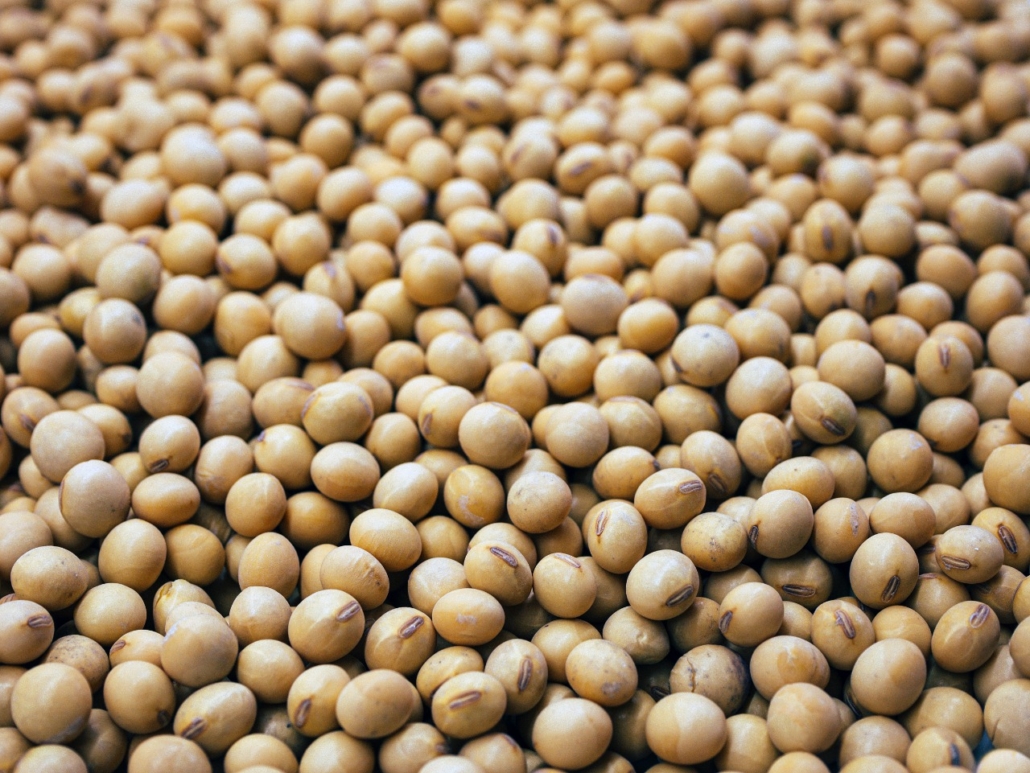

- Another excellent source of phosphatidylcholine from plants is soy beans. The amount of 214 mg, or 39% of the RDI, is available in one cup (93 grams) of roasted soybeans.
- Additionally, soybeans are a good source of fiber, manganese, magnesium, zinc, and folate as well as plant-based protein.
- To enhance your lecithin intake, try snacking on some roasted soybeans or edamame, the immature form of soybeans.
- For instance, consuming 5 or 10 grams of shiitake mushrooms every day for four weeks lowered inflammatory indicators like C-reactive protein in a study of 52 healthy adults (CRP)
- Researchers found that the generation of crucial immune cells and secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA), an antibody crucial for gut health and immunity, increased in the same study.
Beef
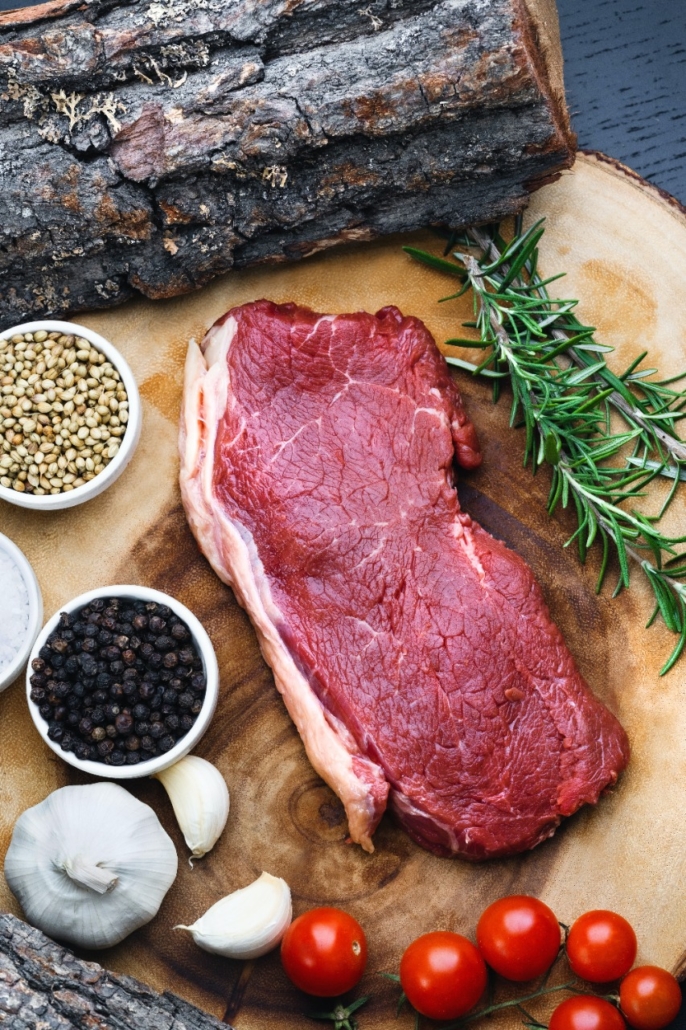

- Phosphatidylcholine is one of the nutrients available in large amounts in beef. A 3-ounce (85-gram) portion of cooked beef has 115 milligrams, or 21% of the recommended daily intake.
- Additionally, beef contains iron and highly accessible protein. Eating beef may help maintain healthy iron stores in the body and increase blood iron levels in anemic persons, who have too few or dysfunctional red blood cells.
Wheat germ
- The best-known use for wheat germ is as a concentrated source of fiber. Additionally, it contains a wealth of essential nutrients like lecithin, manganese, magnesium, zinc, and vitamin E.
- 153 mg of phosphatidylcholine, or 28% of the RDI, may be found in just 3 ounces (84 grams) of toasted wheat germ.
- To add choline and satisfying fiber to your meals and snacks, stir wheat germ into yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothies.
Cruciferous vegetables
- Choline is in some cruciferous vegetables, including cauliflower, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
- Compared to cooked Brussels sprouts and broccoli, which each contain about 30 mg, or 5% of your daily needs, one cup (160 grams) of cooked cauliflower contains 72 mg, or 13% of your daily needs.
- To fulfill your daily requirements for this vitamin, combine have cruciferous vegetables with other choline-rich meals like salmon, eggs, chicken, beef, or turkey.
Almonds
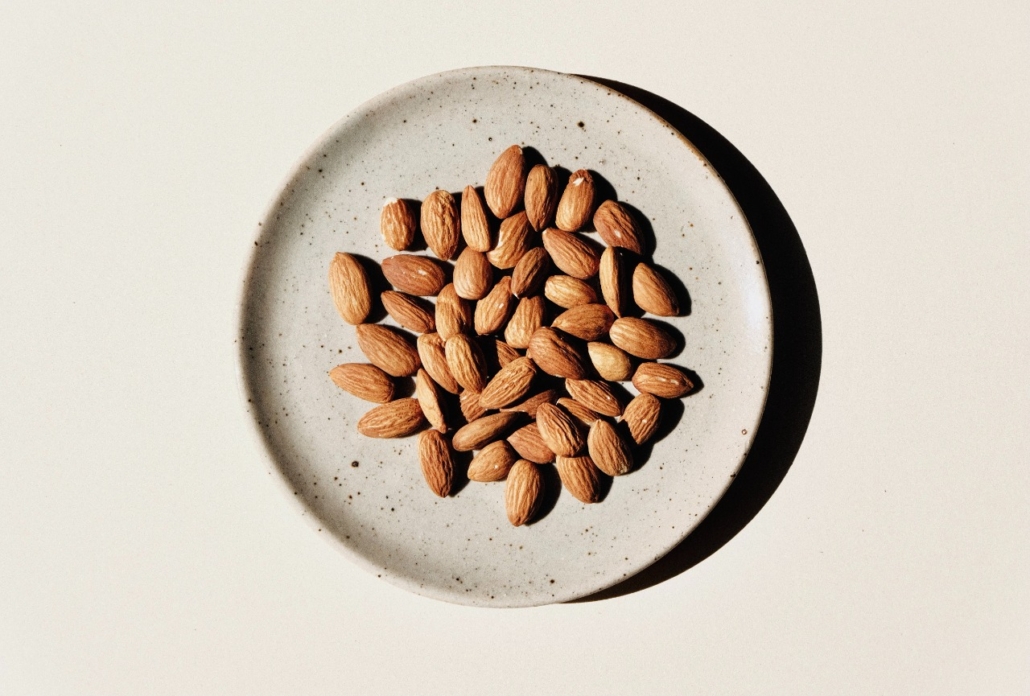

- Almonds, a common tree nut, are well-known for their many health benefits. The numerous health benefits of common tree nuts like almonds are well known. As an illustration, studies have shown that consuming them may increase levels of heart-protective HDL cholesterol and support a healthy body composition.
- Additionally, they contain high amounts of magnesium, protein, fiber, and vitamin E.
- A plant-based source of choline has also been shown to be almonds. About 15 mg of the vitamin are found in 1 ounce (28 grams) of almonds, which is 2.5% of your daily requirements.
Quinoa
- Quinoa is a well-known gluten-free pseudo cereal. It is a good source of choline and other nutrients.
- 43 mg, or 8% of the RDI, of the vitamin are present in one cup (185 grams) of cooked quinoa.
- Conveniently, quinoa is adaptable and can be pair with other foods to make delectable meals that are rich in choline.
- For a tasty, choline-rich breakfast alternative, consider cooking a morning hash with eggs, broccoli, and red potatoes and serving it over cooked quinoa.
Give us order click phosphatidylcholine.
Check our latest product click here.